Saturday, September 25, 2010
Engage Me!
Questionnaire #3
Having read so much over the past months about Inquiry Based Learning, I find myself reflecting on statements by people such as Chen (2003), who suggests that "Learning occurs only when the learners are actively involved in the construction and reorganization of concepts..." as well as Phye (1997) who says that Inquiry based learning "...combines congnition from a developmental perpective with other important issues, such as motivation, self-directed learning and a focus on the social context of learning". These statements both imply that what we need to teach children needs to be made interesting and important to them.
2. How interested are you in this topic?
a great deal
3. How much do you know about this topic? Circle the answer that best matches how much you know.
Quite a bit - still lots to learn
4. Thinking back on your project, what did you find find easy to do?
Start thinking of ideas to take into the classroom to use with the children.
5. Thinking back on your project, what did you find most difficult to do?
I still find refining of searches difficult to do. Taking the project back into the classroom, I found it very difficult to help the children with learning difficulties to open up and use the variety of search tools effectively. It was also difficult helping them to come up with "researchable questions".
6. What did you learn in doing this research project?
I learned that the way we teach and structure our learning tasks for children has a huge impact on what they come away with. I learned that it is important to allow children to falter as they move along in their learning journey, to enable them to get the most out of what they have learned. By the same token, I also beleive that this method of teaching is not suitable for all children, as much as the experts say it is. I observed a few of the children in my Year 7 class who have learning difficulties become very frustrated and agitated during the process and this hindered their ability to find the information they wanted as they felt quite helpless at times. With these children one needs to guide them a lot more and even supply the places where they may find the information. The information they find is not always easily accessible to them due to their levels of reading and comprehension. Sometimes it may be that we need to guide children like this to the answer. I realise that this is open to debate and that I may be "shot down" for making these suggestions, but sometimes reality bites!
Questionnaire #2
At this stage, I have come to realise that this way of teaching or at least getting children to research has been a minor part of my teaching anyway. I have used guided inquiry type methods, with a little more "guidance" than is required, as the children are not that used to having to come up with the questions themselves. I am motivated by what I am reading about guided inquiry and am very keen to make it a more prominent part of my teaching in the classroom. I now realise that htere are a multitude of models out there, ranging from my favourite, Kuhlthau to the more drawn out model of Eisenberg and Berkowitz.
How interested are you in your topic?
Very interested
How much do you know about your topic?
A fair amount
When you research, what do you find easy to do?
I find it easy to find a lot of generalised information.
When you research, what do you find difficult to do?
I still find it incredibly difficult to refine my searches, knowing what I definitely need in the search and what to exclude. I can only imagine how difficult it must be for the children to research if I am finding it challenging, especially when it is an unknown topic, or a topic that is something I know very little about.
Monday, September 6, 2010
The quest for the ulitmate question...
Strategy Three - The Daily Research Question
Each day begins with students walking into the classroom to note an intriguing research question on the board. Puzzles, riddles and curious questions that can be answered reasonably well without months of study. These should require some thought and ingenuity, not be mere trivial pursuit. They should be highly motivating and captivating.
The only thing is, to formulate these highly motivating and captivating questions...
Saturday, September 4, 2010
Inquiry based project in the classroom
Narrowing the search with Boolean logic


I discovered a great site which can be used with children to teach them Boolean logic in searching for information. The site is boolify.org It is a simple tool to use and children can easily see when their searches result in too many or too few results.

I typed in inquiry based projects and upper primary school and came up with one result which was totally unrelated to the information I was looking for. My next attempt was to type in inquiry based projects AND primary school OR elementary school which produced 138 results, wishing to narrow the search down, I backtracked and removed the OR elementary school, which produced 37 results which was far more manageable, but there were many unuseful results. Again I backtracked and typed in inquiy based projects AND english AND primary school, which produced 29 results - but none of the results proved useful. I have concluded that it is too difficult to actually narrow down inquiry based projects in english, but to look for broader searches and adapt that information to the project set for the students in my class.
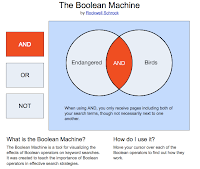
On further searches for tools to use to teach children, I discovered Rockwell Schrock's website entitled The Boolean Machine, which explains quite clearly the use of AND, OR and NOT. See illustrations above.
YIPEE!
Using the search engine Yippy I did indeed say "yippee" as I came across a site called "iBreadcrumbs - The first way to save and share online research" http://www.ibreadcrumbs.com/user/cathyinoz/Inquiry-based_learning/ The first topic was Inquiry Based Learning. There, I read about an interesting man, John Barrell who is an author and an expert on inquiry-based learning. Now that in itself does not sound like anything mind shattering, but clicking the link at the bottom of the page : http://www.morecuriousminds.com/ I discovered that he had developed so many questions about heros of the South Pole, that he decided to sail to Antarctica to satisfy his cuiriosites. It did not end there, he subsequently "...became an educator attempting to explore the many possibilities for educating young people in non-traditional settings..." His writings reflect an attempt to challenge students and their teachers to take risks by adventuring into complex situations to inquire, solve problems and think critically. Although we are unable to take our students on real wild adventures, the implications are that we should take them on these adventures using all the tools available to us as educators. He suggests the use of literature, objects, films, and other representations of experience, which correlates well with the GeSt Windows of information. He outlines Inquiry-Based instruction in an article "Why are School Buses Always Yellow?" (2007)and "Developing More Curious Minds (Barrell,2003)
And so the search continues
After having typed in a search for "information search process" I came across a great site called "information Age Inquiry" which provides a broad outline and links to a variety of Information Inquiry Models:
Kuhlthau's ISP:
1. Initiating a Research AssignmentFeelings: apprehension, uncertainty
2. Selecting a TopicFeelings: confusion, sometimes anxiety, brief elation, anticipation
3. Exploring InformationFeelings: confusion, uncertainty, doubt, sometimes threat
4. Formulating a FocusFeelings: optimism, confidence in ability to complete task
5. Collecting InformationFeelings: realization of extensive work to be done, confidence in ability to complete task, increased interest
6. Preparing to PresentFeelings: sense of relief, sometimes satisfaction, sometimes disappointment
7. Assessing the ProcessFeelings: sense of accomplishment or sense of disappointment
Ian Jukes 5 A-s model:
1. Asking - key questions to be answered
2. Accessing - relevant information
3. Analyzing - the acquired information
4. Applying - the information to a task
5. Assessing - the end result and the process
Michael Eisenberg and Robert Berkowitz' Big 6 (older students) and Super 3 (young students):
The Big 6 is an information problem-solving approach developed by Michael B. Eisenberg and Robert E. Berkowitz. It is the most popular model for information skills. It includes the following steps:
1. Task definition
2. Information seeking strategies
3. Location and access
4. Use of information
5. Synthesis
6. Evaluation
Although The Big 6 only includes six steps, some primary teachers find it overwhelming for their young learners. As a result, teachers have developed modified versions to meet their needs. Eisenberg and Berkowitz have developed a version called the Super 3 for very young children. It includes three steps:
1. Plan
2. Do
3. Review.
There were many other models described on this site which gave me quite a broad overview of the similarities and differences between the different models. I still think, though, that Kuhlthau's model is the most practical sounding model to use with the group of children I have at present.
Monday, July 26, 2010
Reflections
Questionaire #1
1. What do I know about my topic?
I have a very generalised (sparse) understanding of Inquiry Based Learning, although for years I have believed that I have been leading my students through this approach to research - we will have to see...
2. How interested am I in this topic?
Very interested
3. How much do I know about this topic?
I know that as a teacher (or guide in this instance, I need to know a LOT more to be able to guide the children effectively to get the most out of their acutal guided inquiries.)
4. When I do research, what do I generally find easy to do?
I find it very easy to find answers to my questions, as well as find a lot of resources to use to illustrate my findings.
5. When I do research, what do I generally find difficult to do?
I find it difficult to analyse and synthesise information at times. I also find it difficult to stop searching once I start - it is like a bug - once I start finding good information, it is hard to simply decide that I have enough resources, links and information.
A journey through guided inquiry and inquiry based learning
Upon typing in my search for "inquiry based learning + elementary", I came across a variety of interesting articles on a page called "Youth Learn" (http://www.youthlearn.org/learning/general-info/our-approach/intro-inquiry-learning/intro-inquiry-learning)which discusses technology, media and project-based learning to inspire young minds. Yes! I think I have finally found something of interest... I think the key to doing inquiry based learning is that the questions the children chose have to be questions they honestly care about. These questions should be such that they actually encourage the children to ask more questions along the way. Although this whole approach is founded on children taking the lead in their own learning, it still requires us as guides to be well planned with goals to be reached. There is a fear that inquiry based learning my be too unstructured, but this is definitely not the case, as they require the teacher to be even better planned and prepared - the major difference is that the teacher's role is vastly different, not the actual learnng process. The following diagram (Morino Institute 2010) illustrates the inquiry process:

An interesting game(from the abovementioned site) "The Question Game" would be one I would like to try:
Try playing The Question Game with your kids. To start, two participants decide on a topic to question. One person starts with an open-ended question, then the other person responds with a related open-ended question. This goes back and forth as long as they can continue without making a statement or repeating a previous question.